Back Pain in Adolescents vs. Back Pain in Adults
Many of us think of back pain as an older person’s problem. That’s not surprising actually, because most back problems occur between the ages of 35 and 55, and are the result of natural processes associated with aging, such as degenerative disc disease or sciatica. But back pain can also affect adolescents, and even children. In fact, by the time they are 20, as many as half of all young people will have experienced back pain. The pain my be sharp and shooting, burning or aching, and may be felt anywhere in the back. Here at New Jersey Spine Specialists, we see young patients from northern New Jersey and beyond who come to us because of back pain, and their parents invariably ask, is there a difference in the causes of back pain in adolescents and back pain in adults? The short answer is, yes, the causes of adolescent back pain are usually different than adults’.
Treatment for Back Pain in Adults and Adolescents
In adolescents, as in adults, benign musculoskeletal diseases and trauma are responsible for most cases of back pain. Sports or play, carrying a heavy back pack, or falling, can all strain or sprain muscles in the back resulting in pain. Among younger patients seen in hospital emergency rooms with back pain, trauma and muscle strain account for about half of the cases. In fact, studies indicate that in at least half of cases of adolescent back pain the exact cause is never identified. Fortunately, simple palliative therapies such as physical therapy, avoiding strenuous activity and medication are effective in relieving symptoms, and most cases of back pain in adolescents are not serious and resolve without treatment.
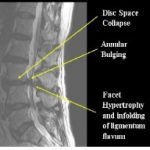
While most causes of back pain in adolescents will resolve on their own, there are some more serious conditions that need to be identified. A stress fracture of the spine is known as spondylolysis and it can occur with or without spondylolisthesis, which is forward slippage of one vertebra on another. Lumbar disc herniations can also occur in adolescents. Spinal deformities such as scoliosis and kyphosis may manifest themselves during the adolescent growth spurts. Congenital and acquired conditions including infections, inflammatory diseases, and tumors can also cause back pain in children and adolescents.
If your teenager is experiencing back pain, the good news is that it will most likely get better on its own. A physician specializing in disorders of the spine, such as a spinal orthopedic surgeon, can help properly diagnose and treat the back conditions that do require medical intervention.